Welcome to the Network Engineers training tutorials by CoreNetworkZ Tech Solutions. Today, I will teach you a Command Line tool, Tracert, and its practical uses.
The Tracert command (Trace Route) helps determine the path from your computer to the destination host by sending ICMP Echo Request messages.
Once the command finds the path to the destination, it will print it on the command prompt. Now you understand why the Trace Route (Tracert) utility is popular.
Tracert prints the route to the destination IP.
This tutorial covers the application of the Tracert (Trace route) utility in troubleshooting a connection problem.
How Does Trace Route (Tracert) Help To Fix Network Problems?
I have read a few comments asking about the practical uses of this command line tool. Samuel Roukin is one of them. He wanted to know how the tracert command helps technicians fix connectivity issues.
ICMP command Tracert is very helpful to troubleshoot network-related issues. It helps determine the network location where the actual cause of the issue is present.
Let us check how it works.
It sends ICMP Echo messages to the destination host and decrements its TTL value by one when it passes on each hop. When the packets pass each hop, it displays the path in the DOS window. So you can identify the route.
This feature helps to identify the actual cause of any network issue. So, it is a handy tool for every network Engineer to analyze and troubleshoot network issues. Let us check how to use this tool.
How to Print the Path To a Remote Device On Command Prompt?
Xander asked me in the comment section about printing the route from his PC to a remote server. It is an easy task. Xander, you can print the route by executing the tracert command on the DOS window.
The primary application of the Tracert utility is to trace and print the path to a remote server. Let me explain the procedure.
Open Command Prompt.
Type the following command and press the enter key.
tracert remote IP
Remote IP is the IP address or the domain name. You will see the path to the remote IP address from your computer.
A Practical Example of Printing Route To a Website
If you want to know the route of the server of www.corenetworkz.com from your computer, you can check it by typing the following code on the DOS prompt.
Tracert www.corenetworkz.com
You can see the result in the screenshot.
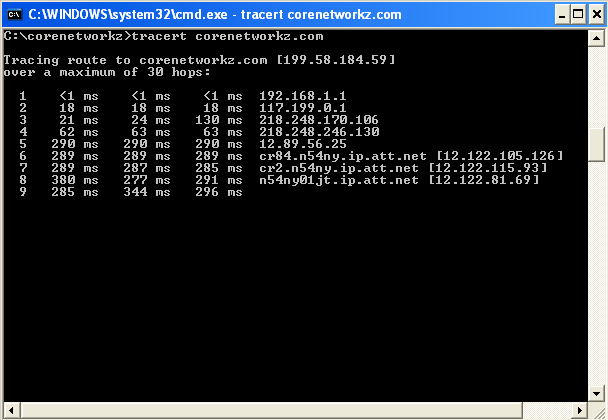
We use the Tracert command to find the path and deliver the packets to the destination host from the source. Now, let us check the general syntax of the tracert command.
The general syntax is :
tracert [-d] [-h MaximumHops] [-j HostList] [-w Timeout] [TargetName]
Ajith Thomas and Muhammed Rameez asked about setting a maximum hop count with the tracert tool. I suggest they read the general syntax I published and check how to use the -h parameter.
Example: tracert -h 30 google.com
After pressing the enter key, we will have a complete trace of the packet sent. By default, it will go up to 30 hopes. If there is a connection issue, it will show the request timed out when the packet reaches the hop (the one with the problem).
Reference
I suggest the following tutorials to learn more about the command line tool.
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/administration/windows-commands/tracert
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-routed-protocols/22826-traceroute.html


Hi Alex,
ReplyDeleteI have question for you. How do I write a tracert code to send packets Instagram with maximum router number 10?
Hello Ajith,
DeleteYou can set the syntax as: tracert -h 10 www.instagram.com
Hello Alex,
ReplyDeleteIs there any rule to set the maximum number of hops the packets can travel?
Yes Muhammed, we can set the maximum hop count. I explained it in the article.
DeleteThank you, Alex, for writing about this command. But I wonder how this command helps a network technician to solve a connectivity error.
ReplyDeleteHello Samuel,
DeleteI have explained the process in the article.
Does the tracert tool only find the route, or will it show us the route?
ReplyDeleteIt will print the route.
DeleteAlex, can I print the route to Google server from my laptop with this tool?
ReplyDeleteYes, you can Amit.
Delete